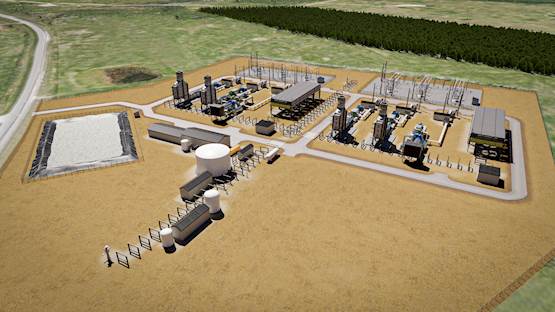
Cache Power, a subsidiary of EPC firm Federation Group, is moving forward with its Marguerite Lake Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES) and Hydrogen Hub Project near La Corey, Alberta, Canada, having awarded an engineering study contract to Babcock & Wilcox (B&W).
The study is partially funded by a grant from Alberta Innovates, a provincial crown corporation tasked with promoting innovation and economic growth in Alberta. The project will incorporate B&W’s BrightLoop energy production and decarbonization technology.
BrightLoop is a flexible chemical looping system that uses a proprietary oxide TranspO2rt particle to produce steam, hydrogen, or syngas while isolating CO₂. The system can process a wide range of fuels and feedstocks, enabling clean energy generation with in-situ CO₂ capture.
The 640 MW CAES facility, sited next to the existing Marguerite Lake substation, will be built in two identical 320 MW phases and provide 48 hours of storage capacity – equivalent to 15,360 MWh each. Renewable energy from the grid will be stored as compressed air in underground salt caverns and later released to generate electricity when demand rises.
To enhance efficiency and reach net-zero emissions, the facility will reheat compressed air with either natural gas or hydrogen before it passes through turbines. BrightLoop technology will generate up to 60 tonnes of hydrogen per day while producing “a nearly pure stream of CO₂ for capture and storage, enabling the project to reach net-zero emissions,” the company said.