New modeling by the Energy Transitions Commission finds that “Sunbelt” countries – including India, Mexico, and much of Africa – are best positioned to reduce power system costs by shifting to low-cost, solar-led energy systems.
“In the global sunbelt, the collapsing cost of solar PV and batteries makes possible far cheaper and more rapid growth in green electricity supply than seemed feasible 10 years ago,” said Adair Turner, chair of the Energy Transitions Commission.
The Energy Transitions Commission said wind- and solar-dominant systems can be stable and resilient with the right mix of balancing and grid technologies, and are no more likely to experience blackouts than thermal-based systems.
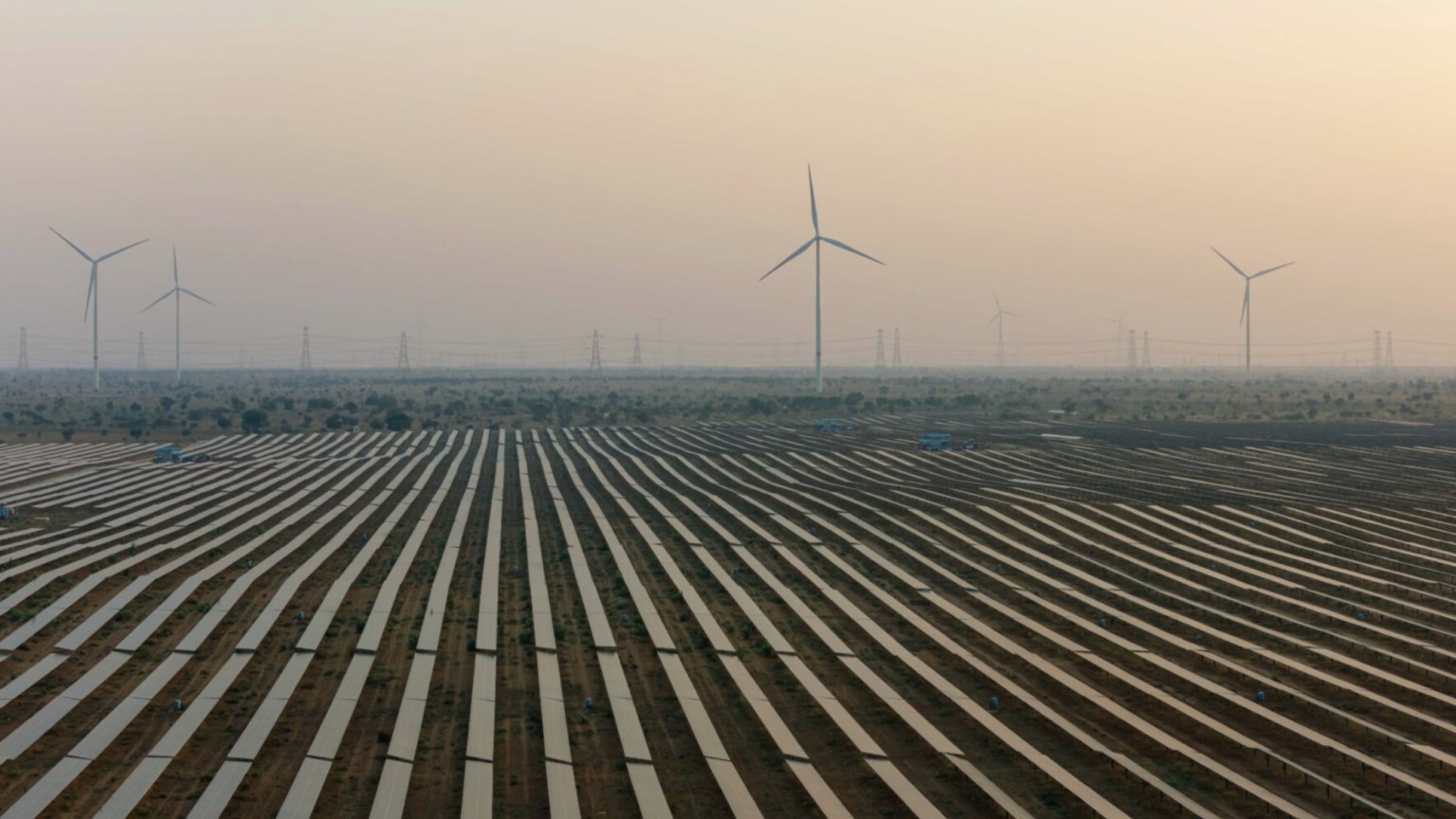
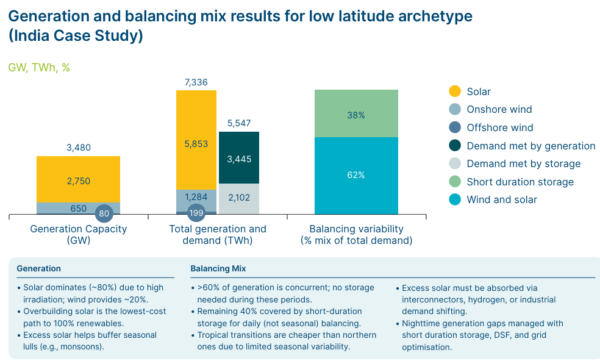
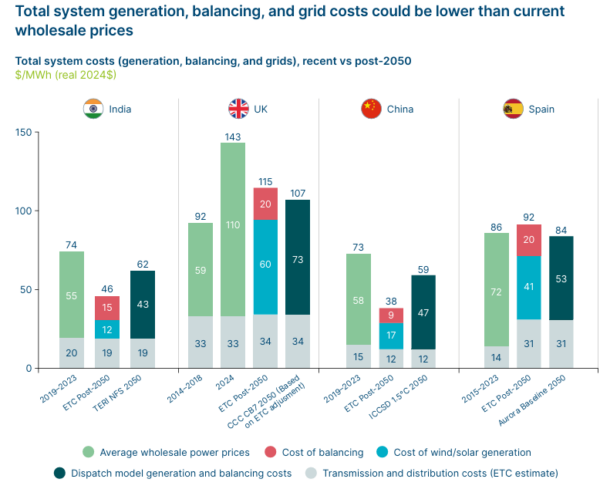
It claimed that India could achieve clean power system at a cost (including generation, balancing, and grid infrastructure) of around $50/MWh by 2050 – significantly below current fossil fuel-driven wholesale prices – by shifting to a fully wind and solar-based electricity system requiring primarily day-night balancing.
The modeling suggests that in such a system, solar would account for approximately 80% of installed capacity with the remainder 20% from wind. By 2050, this setup could generate around 7,300 TWh of electricity annually, comfortably meeting India’s projected demand of 5,500 TWh – more than triple the 2024 consumption of roughly 1,600 TWh.
The report estimates that about 40% of electricity supply would need to be time-shifted using short-duration storage to match demand, due to the system’s heavy reliance on solar.
“The vast majority of this balancing requirement would occur over short durations (intra-day or day-to-day), with minimal need for seasonal or multi-week balancing,” the report said.
The study highlights India’s strong solar resource and falling battery costs. It also notes that India, as a developing economy, can design grid systems optimized for renewables and modern technologies, avoiding legacy constraints faced by developed economies.